Equine Strangles
What is Strangles?
Strangles is an upper respiratory infection caused by the bacteria Streptococcus equi spp. Equi . Infection typically causes fevers, nasal discharge and swollen abscessed lymph nodes around the head and neck.
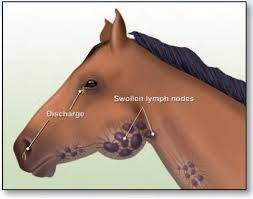
How do horses get infected?
The bacteria is transmitted thru nasal secretions or purulent discharge from abscesses. This can be direct (horse to horse) or indirect (bacterial contamination of buckets, water sources, housing, or on people). The incubation period between exposure and signs of infection is 3 days up to 2 weeks. Horses can remain infectious to other horses weeks. In 10% of cases, a horse can become a chronic carrier of the bacteria, shedding it intermittently in nasal secretions without having outward signs of infection.
Treatment?
The Strangles bacteria is susceptible to treatment with Penicillin and banamine is used to control the fever. However, the nature of the abscess development means that most horses must run through a Strangles infection on their own. Treating with antibiotics before the abscesses rupture can actually prolong the duration of the infection and sometimes increase chances of complications. There are some exceptions though. If a horse develops abdominal Strangles (sometimes called Bastard Strangles) , purpura hemorrhagica, or immune mediated myositis as complications of infection, than aggressive antibiotic treatment is started.
What happens when a horse on a farm gets Strangles?
Strangles is HIGHLY contagious and often many of the horses on the farm will get sick within a few weeks. For this reason, farms with a confirmed outbreak are placed on quarantine. No animals are allowed to leave the farm. Affected or exposed horses must be kept away from unaffected horses. Biosecurity is incredibly important including:
- Changing clothes and shoes after caring for sick animals
- Caring for health animals BEFORE visiting areas occupied by sick animals
- Using only designated equipment for sick animals
- Thorough disinfecting of stalls, buckets, water sources etc throughout and after the end of the outbreak
How do we know when horses are free of the infections?
Horses that have been infected or exposed to Strangles are restricted from movement off the premises for 30 days past the resolution of clinical signs. Often some testing will also be recommended to check for carrier status including serum protein M testing and nasopharyngeal washes.
How can Strangles be prevented?
- Vaccination: There is a vaccine available although it is not 100% effective. Your veterinarian can help you decide if it is necessary for your horses.
- Quarantines: Whenever a new horse arrives at a farm the horse should be quarantined away from other horses for 14 days and watched closely for signs of infection.
Be wary of auctions: Many auction premises consistently battle Strangles on site. Horses coming from these facilities have likely been exposed.